Yield stress vs ultimate stress 235901-Why is breaking stress less than ultimate stress
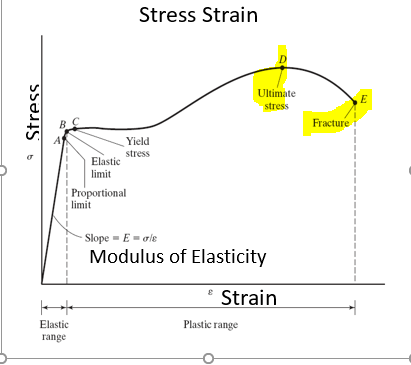
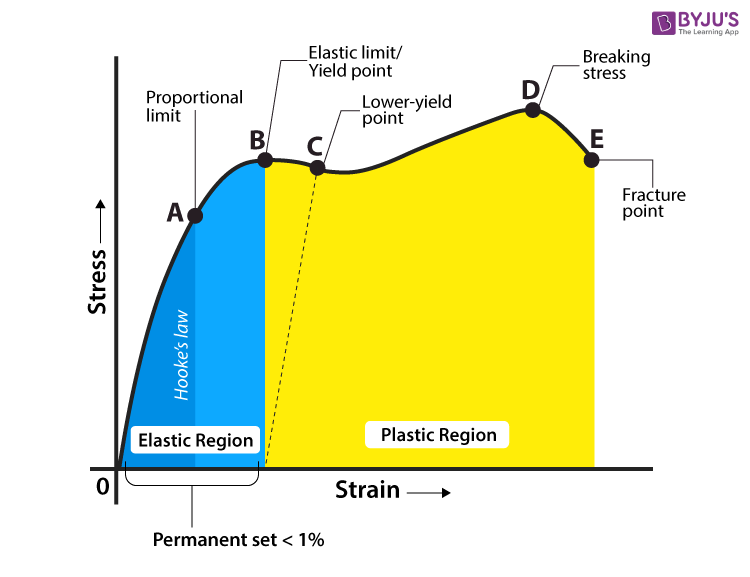
To manage problems related to yield stress, engineers and scientists rely on a variety of formulas dealing with the mechanical behavior of materials Ultimate stress, whether it is tension, compression, shearing or bending, is the highest amount of stress a material can withstandThe stress corresponding to the yield point is called yield point stress The point B is the upper yield stress point and C is the lower yield stress point 4 Ultimate Stress Point It is the point corresponding to the maximum stress that a material can handle before failure It is the maximum strength point of the material that can handle theDepending on the electrode, you can undermatch, overmatch, or match the weld strength to the base material We typically use E70 electrodes which have a yield strength of 70 ksi For wide flanges we typically use 50 ksi steel So when you weld a wide flange given the parameters above, you are overmatching (70 ksi weld vs 50 ksi steel)

Engineering Fundamentals Refresh Strength Vs Stiffness Vs Hardness Fictiv
Why is breaking stress less than ultimate stress
Why is breaking stress less than ultimate stress-Depending on the electrode, you can undermatch, overmatch, or match the weld strength to the base material We typically use E70 electrodes which have a yield strength of 70 ksi For wide flanges we typically use 50 ksi steel So when you weld a wide flange given the parameters above, you are overmatching (70 ksi weld vs 50 ksi steel)Ie 06*UTS If you are looking at YS (Yield Strength) then SYS = 60% of YS;


Determining The Flow Stress Curve With Yield And Ultimate Tensile Strengths Part I
There are three types of tensile strength 1) Yield strength,2) Ultimate strength and 3) Breaking or splitting strength 1) Yield strength the tensile stress of a material can withstand or resist without permanent deformation In other words Yield strength is define as, the stress a material can withstand without permanent deformationFor mechanical engineering strength design applications it is accepted that shear strength is approximately 60% of tensile strength If UTS = 'x' (Ultimate Tensile Strength) This is the value usually reported in handbooks then USS = 60% of 'x';Yield strength is considered when the material is used in the final product, so that the material doesn't deform plastically and remain within the elastic regime Ultimate tensile strength is
Yield strength When subjected to stress, a material undergoes recoverable deformation The yield strength of a material represents the stress beyond which its deformation is plastic Any deformation that occurs as a result of stress higher than the yield strength is permanentUltimate tensile strength is the strength where the necking effect begins Yield strength is the strength where the deformation turns from an elastic deformation to a plastic deformation Yield strength is always lower than the ultimate tensile strengthThe stress corresponding to the yield point is called yield point stress The point B is the upper yield stress point and C is the lower yield stress point 4 Ultimate Stress Point It is the point corresponding to the maximum stress that a material can handle before failure It is the maximum strength point of the material that can handle the
Yield strength When subjected to stress, a material undergoes recoverable deformation The yield strength of a material represents the stress beyond which its deformation is plastic Any deformation that occurs as a result of stress higher than the yield strength is permanentYield strength or yield stress is the material property defined as the stress at which a material begins to deform plastically whereas yield point is the point where nonlinear (elastic plastic) deformation begins Prior to the yield point, the material will deform elastically and will return to its original shape when the applied stress isThe ultimate stress for brittle material is considered as ultimate tensile strength and for ductile material is considered as yield strength Also, as the equation for factor of safety is the ratio of two stress or load values, it is dimensionless The difference between the Factor of Safety and 1 is known as Margin of safety
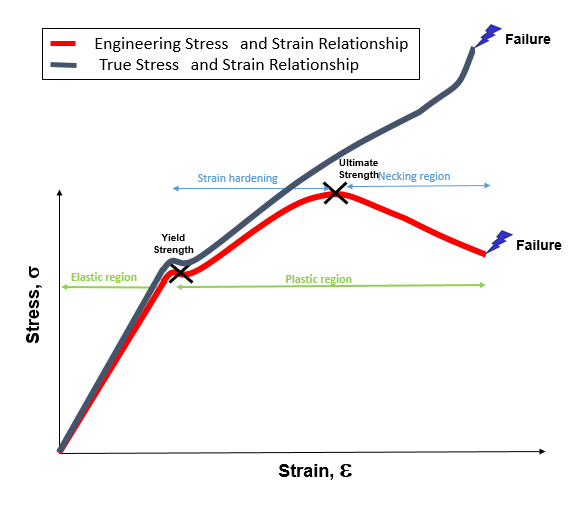


Engineering Stress Strain Vs True Stress Strain Yasin Capar
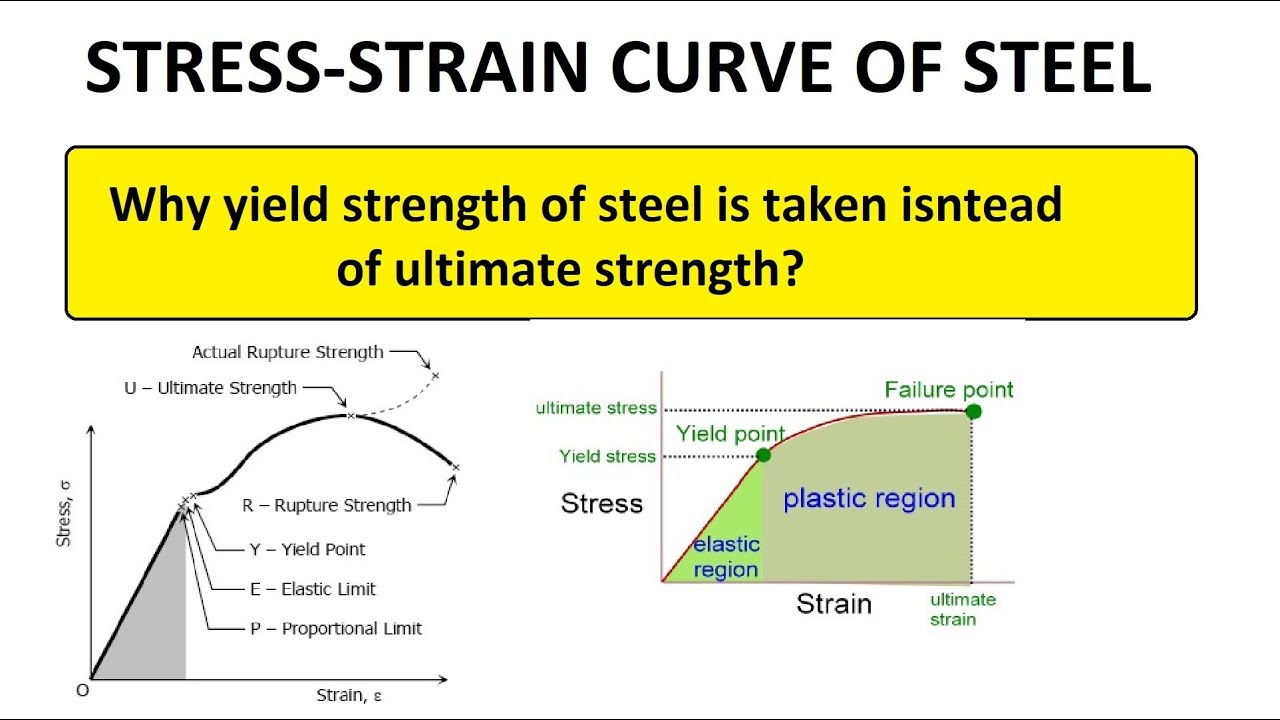


Hindi Stress Strain Curve For Steel Yield Strength Vs Ultimate Strength Youtube
Limit, yield strength have been used for the first property For the failure stress such terms as ultimate strength, strength, rupture, and limiting stress and many more have been used All of these have had rather different interpretations None have been entirely satisfactory and none universally adoptedYield strength is used in materials that exhibit an elastic behavior It's the maximum tensile stress the material can handle before permanent deformation occurs Ultimate strength refers to the maximum stress before failure occurs Fracture strength is the value corresponding to the stress at which total failure occursThere may be situations where yield or proof strength values of steel are known, but ultimate tensile strength (UTS) values have not been reported As the knowledge of UTS is important for quantifying strainhardening properties, an estimation scheme has been developed under the European project SINTAP 1



Stress Strain



Mechanics Ebook Failure
Yield strength is the stress which will cause a permanent deformation of 02% of the original dimension Ultimate Strength The ultimate strength of a material is the maximum stress a rope or material can withstand Breaking Strength Breaking strength refers to the stress coordinate on the stressstrain curve at the point of ruptureHence generally, failure of a material is assumed when the Yield strength is exceed However, beyond Yielding, does Von Mises stress actually tell you anything about Rupture of the material which is what those of us that do assess structures against ultimate strength really do worry aboutThe definition of stress that takes the continuous change in the area into account is called true stress Difference between Yield Strength and Tensile Strength Definition Yield strength is the stress that causes a material to lose its elastic behaviour Tensile strength is the maximum stress that a material can handle before breaking



Yield Strength Strength Mechanics Of Materials Engineers Edge



Plotstressstrain File Exchange Matlab Central
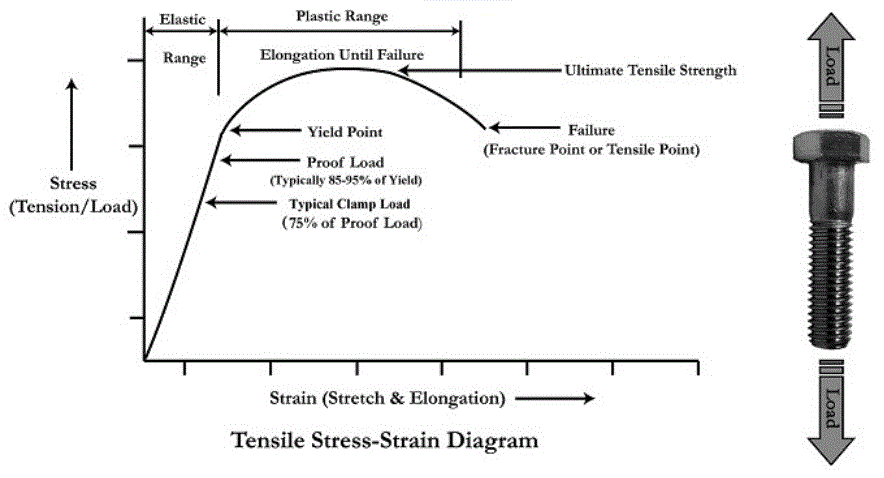
Stress is force per unit area that results from an applied load Strain is a physical deformation response of a material to stress Allowable Stresses Concrete is 045 f'c Steel is 060 fy 2 Ultimate Stress Design Ultimate stress design is also known as Strength Design Method It considers the plastic limit of stresses in designYield strength indicates maximum stress or load that a solid material can withstand when it is deformed within its elastic limit On the other hand, ultimate strength indicates the maximum stress or load withstanding capability of a material when it is plastically deformedThe ultimate tensile strength is the maximum stress level on the engineering stressstrain curve, ie the maximum stress that can be withstand by a structure in tension All deformation before this point is uniform throughout the narrow region of the material



Ultimate Tensile Strength Wikipedia



What Is The Von Mises Stress And The Yield Criterion
Yield strength is the stress which will cause a permanent deformation of 02% of the original dimension Ultimate Strength The ultimate strength of a material is the maximum stress a rope or material can withstand Breaking Strength Breaking strength refers to the stress coordinate on the stressstrain curve at the point of ruptureWhile the ultimate tensile strength of a material is higher than the yield strength, it is a condition that hopefully your fasteners will never see as it represents catastrophic failure or the equivalent of ripping off the arm wrestlers arm Figure 1 shows the relationship of yield strength to ultimate tensile strengthA fastener's tensile strength, or ultimate tensile strength, is the force at which the fastener fractures To test tensile strength, we use a wedge tensile test, where a wedge is placed under the head of the fastener and force is applied until the fastener breaks A wedge tensile test looks like this



Strength At Break Tensile



Casing Design Theory And Practice Material Properties Definition Drilling Manual
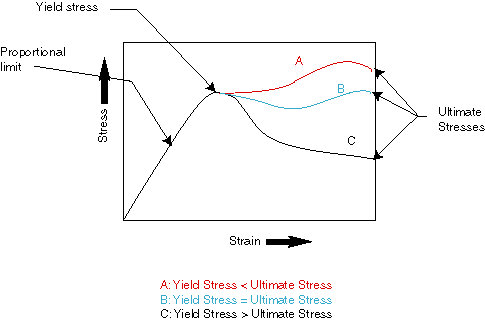
There are three types of tensile strength 1) Yield strength,2) Ultimate strength and 3) Breaking or splitting strength 1) Yield strength the tensile stress of a material can withstand or resist without permanent deformation In other words Yield strength is define as, the stress a material can withstand without permanent deformationShould the yield strength (σ γ) be equal to the ultimate tensile strength (UTS), any plastic deformation of the pipe could result in rupture However, with a difference between σ γ and UTS, the ability for the steel to exhibit strain hardening provides some protection for the pipe against fracture, for example, during layingYield Strength, Modulus of Elasticity, Ultimate Strength of Selected Materials A straight line is drawn through Point (D) at the same slope as the initial portion of the stressstrain curve The point of intersection of the new line and the stressstrain curve is projected to the stress axis


What Is The Difference Between Ultimate Stress And Yield Stress Quora


Determining The Flow Stress Curve With Yield And Ultimate Tensile Strengths Part I
Should the yield strength (σ γ) be equal to the ultimate tensile strength (UTS), any plastic deformation of the pipe could result in rupture However, with a difference between σ γ and UTS, the ability for the steel to exhibit strain hardening provides some protection for the pipe against fracture, for example, during layingYield strength is considered when the material is used in the final product, so that the material doesn't deform plastically and remain within the elastic regime Ultimate tensile strength isYield strength is used in materials that exhibit an elastic behavior It's the maximum tensile stress the material can handle before permanent deformation occurs Ultimate strength refers to the maximum stress before failure occurs Fracture strength is the value corresponding to the stress at which total failure occurs
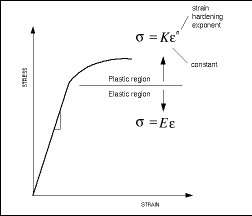


Importance Of Yield Strength Plastic Deformation To Civil Engineers


Strength And Stiffness Characteristics
Triaxial stress (equivalent stress) is not a true stress It is a theoretical value that allows a generalized threedimensional (3D) stress state to be compared with a uniaxial failure criterion (the yield strength) In other words, if the triaxial stress exceeds the yield strength, a yield failure is indicatedLimit, yield strength have been used for the first property For the failure stress such terms as ultimate strength, strength, rupture, and limiting stress and many more have been used All of these have had rather different interpretations None have been entirely satisfactory and none universally adoptedCompressive yield stress is measured in a manner identical to that done for tensile yield strength When testing metals, it is defined as the stress corresponding to 0002 in/in plastic strain For plastics, the compressive yield stress is measured at the point of permanent yield on the stressstrain curve
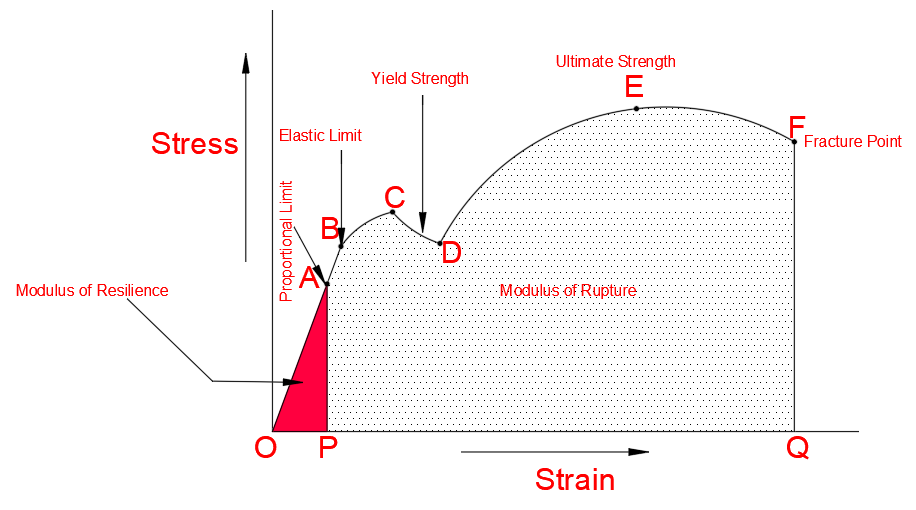


Stress Strain Curve For Mild Steel Explained Civilmint
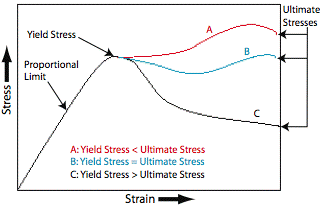


Design In Strength Of Materials Materials Links Resources Plastics
USS Ultimate Shear Strength, UTS Ultimate Tensile Strength, SYS Shear Yield Stress, TYS Tensile Yield Stress There are no published standard values for shear strength like with tensile and yield strength Instead, it is common for it to be estimated as 60% of the ultimate tensile strengthAllowable Stress (Strength) The allowable stress or allowable strength is the maximum stress (tensile, compressive or bending) that is allowed to be applied on a structural material The allowable stresses are generally defined by building codes, and for steel, and aluminum is a fraction of their yield stress (strength)There are three types of tensile strength 1) Yield strength,2) Ultimate strength and 3) Breaking or splitting strength 1) Yield strength the tensile stress of a material can withstand or resist without permanent deformation In other words Yield strength is define as, the stress a material can withstand without permanent deformation
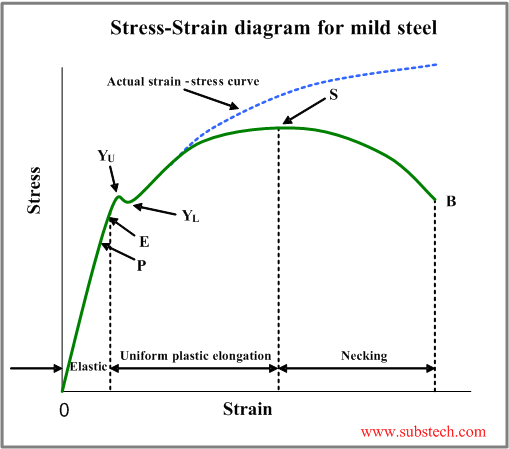


Tensile Test And Stress Strain Diagram Substech
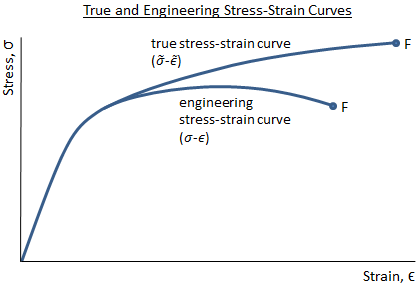


Mechanical Properties Of Materials Mechanicalc
The ultimate stress for brittle material is considered as ultimate tensile strength and for ductile material is considered as yield strength Also, as the equation for factor of safety is the ratio of two stress or load values, it is dimensionless The difference between the Factor of Safety and 1 is known as Margin of safetyView How to convert load vs displacement curve to stressUltimate tensile strength is often shortened to "tensile strength" or even to "the ultimate" If this stress is applied and maintained, fracture will result Often, this value is significantly more than the yield stress (as much as 50 to 60 percent more than the yield for some types of metals)


Solved Matlab Code To Determine The Ultimate Stress And F Chegg Com



Yield Point Instron
Yield strength is used in materials that exhibit an elastic behavior It's the maximum tensile stress the material can handle before permanent deformation occurs Ultimate strength refers to the maximum stress before failure occurs Fracture strength is the value corresponding to the stress at which total failure occursYield strength is the maximum stress that can be applied before it begins to change shape permanently This is an approximation of the elastic limit of the steel If stress is added to the metal but does not reach the yield point, it will return to its original shape after the stress is removedYield stress is the stress at which that the material deforms permanently, ultimate tensile stress is the stress at which it breaks There is probably some official ISO/ASME definition of how much it has to deform for it to count as having yielded



Stress Strain Relations Tensile Testing Yield Ultimate Strengths Elastic Modulus Safety Factor Youtube
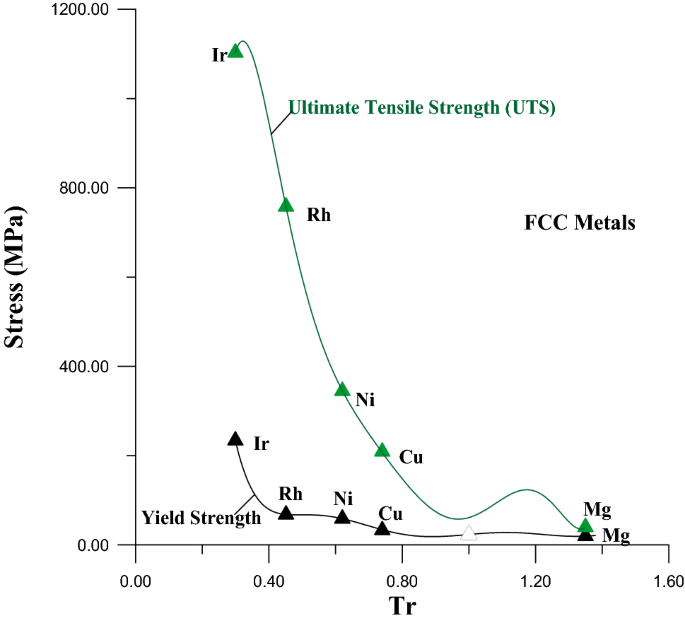


Estimation Of The Ultimate Tensile Strength And Yield Strength For The Pure Metals And Alloys By Using The Acoustic Wave Properties Scientific Reports
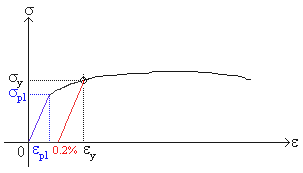
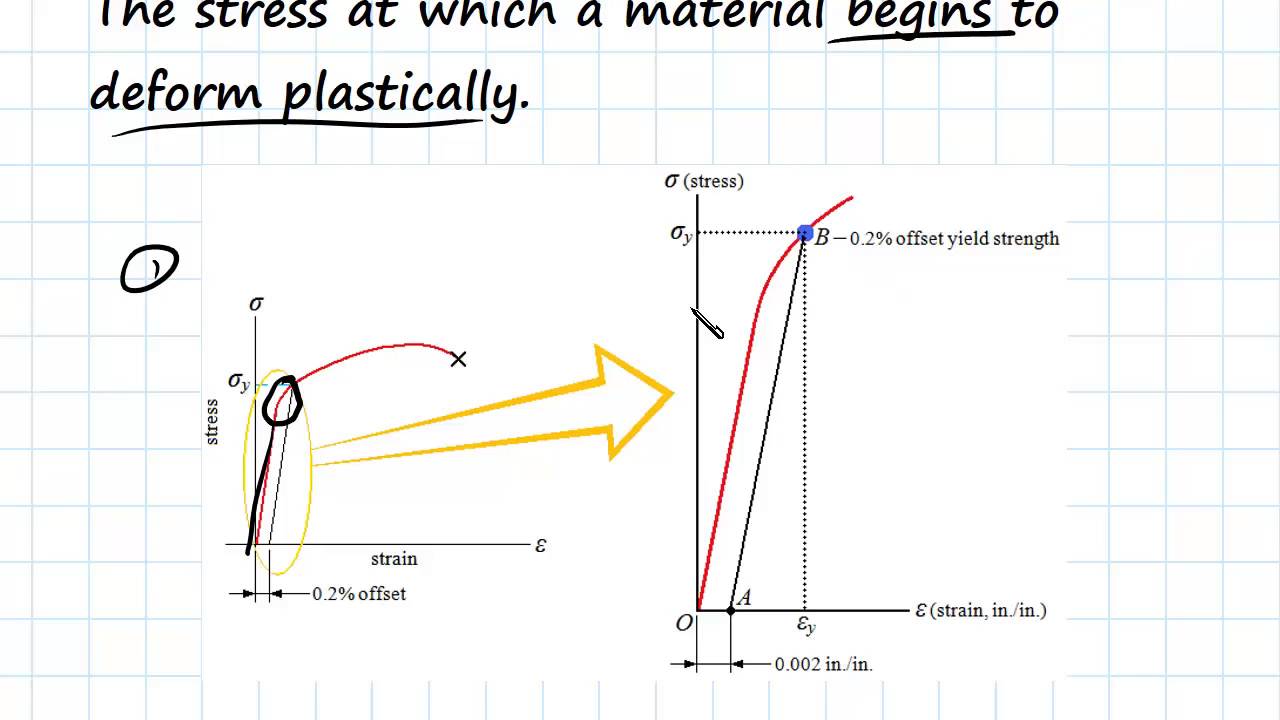
Yield strengths and other specifications are intended only as a basis for comparison This information is not guaranteed, you should be advised to consult with an engineer Source wwwmatwebcomThe yield strength is defined as the stress required to produce a small, amount of plastic deformation The offset yield strength is the stress corresponding to the intersection of the stressstrain curve and a line parallel to the elastic part of the curve offset by a specified strain (in the US the offset is typically 02% for metals and 2%Ultimate tensile strength (UTS), often shortened to tensile strength (TS), ultimate strength, or within equations, is the maximum stress that a material can withstand while being stretched or pulled before breaking In brittle materials the ultimate tensile strength is close to the yield point, whereas in ductile materials the ultimate tensile strength can be higher


Yield Strength Definition Examples Stress Strain Graph Faqs



What Is The Difference Between Ultimate Stress And Yield Stress Quora
The stress corresponding to the yield point is called yield point stress The point B is the upper yield stress point and C is the lower yield stress point 4 Ultimate Stress Point It is the point corresponding to the maximum stress that a material can handle before failure It is the maximum strength point of the material that can handle theYield Strength, Modulus of Elasticity, Ultimate Strength of Selected Materials A straight line is drawn through Point (D) at the same slope as the initial portion of the stressstrain curve The point of intersection of the new line and the stressstrain curve is projected to the stress axisYield strength or ultimate tensile strength?



Engineering Fundamentals Refresh Strength Vs Stiffness Vs Hardness Fictiv



A Tensile Stress Strain Curves B The Yield Strength Elongation Download Scientific Diagram
For knowing the tensile property of friction stir welded sample which is more important;The material then undergoes transformation where stress is not in direct proportion to the strain when a state of yielding (a neck formation) just forms which is the ultimate stress Thereafter the stress that is applied to the material during the yield stage causes the material to snap or breakYield strength is the maximum stress that can be applied before it begins to change shape permanently This is an approximation of the elastic limit of the steel If stress is added to the metal but does not reach the yield point, it will return to its original shape after the stress is removed


Stress Strain Curve Wikipedia



What Is The Relationship Between Ultimate Tensile Strength Young Modulus And Elongation At Break


Elastic Limit Yield Stress Ultimate Stress Breaking Stress Elasticity Elastic Constants Modulus Of Elasticity Young S Modulus Modulus Of Rigidity Shear Modulus Bulk Modulus Working Stress Hooke S Law Modulus Of Elasticity Young S Modulus Limit Of


Determining The Flow Stress Curve With Yield And Ultimate Tensile Strengths Part I



Yield Stress Vs Critical Load Stress Engineering Stack Exchange


Engineering Purdue Edu Xe Forms for website Fe review Slides Problemsandsolution1 Material science Problems Pdf


Plastics


Civl 1101


Variation Of A Yield Stress And B Ultimate Stress Of Type Aisi 316 Download Scientific Diagram



Tensile Strength And Elongation At Yield Astm D638



Shear Yield Strength An Overview Sciencedirect Topics


Http Web Mit Edu Dlizardo Www Uniaxialtestinglabreportv6 Pdf



Meam Design Meam247 09a Uniaxialstrain



How To Measure Tensile Strength Elastic Modulus And Ductility Rolled Alloys Inc



Estimating Tensile Strength From Yield Or 0 2 Proof Values Twi



Why Does The Stress Strain Curve Decrease Engineering Stack Exchange


What Is The Difference Between The Yield Strength Re And The Practical Limit Rp Of A Material Quora
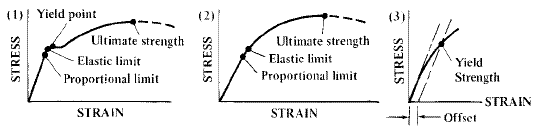


Strength Of Materials Basics And Equations Mechanics Of Materials Engineers Edge



Yield Strength Engineer Educators Com



Yield Stress Of A Material Simple Explanation Civildigital



Ultimate Tensile Strength Uts Stress Strain Curve



Minimum Yield Strength An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



Stress Strain Curve Strength Of Materials Smlease Design



Question Regarding Ultimate Limit State Design Structural Engineering General Discussion Eng Tips


Stress Strain Behavior Of Polymers



Strength At Break Tensile



Sheet Metal Tension Testing Admet


Tensile Strength Soft Matter
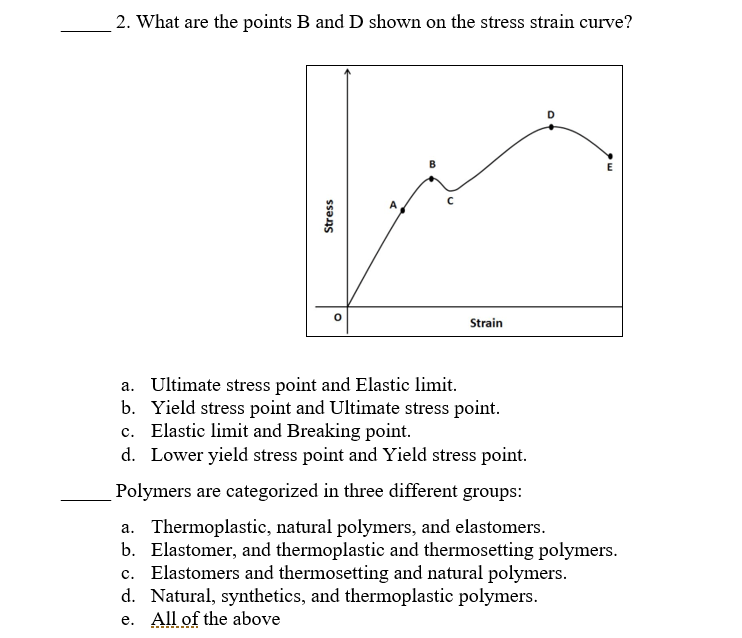


Solved 2 What Are The Points B And D Shown On The Stress Chegg Com



Solved Problem 1 Find The Ultimate Tensile Strength An Chegg Com


What Is The Difference Between Ultimate Stress And Yield Stress Quora



Yield Strength Strength Mechanics Of Materials Engineers Edge


Correlation Between Engineering Stress Strain And True Stress Strain Curve


Q Tbn And9gcrdlwvzddnehsqd3q4pa68yhsrtz2zujhc4jj P3hg9jteevyia Usqp Cau


Http Www Csun Edu Bavarian Courses Mse 227 Labs 4 Tension Test Pdf
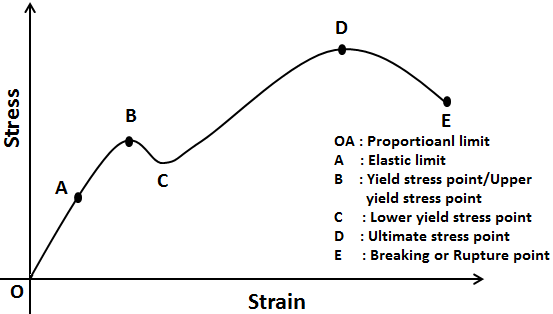


Stress Strain Curve Myrank



Yield Stress And Ultimate Tensile Stress As A Function Of Temperature Download Scientific Diagram
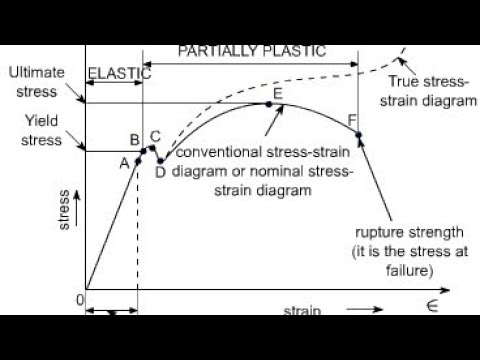


Stress Vs Strain Curve Yield Point Yield Strength Elastic Limit Neking Ultimate Tensile Youtube



Meam Design Meam247 09c P2



How Come The Yield Strength Is Greater Than Tensile Strength When Testing A Steel Specimen Quora
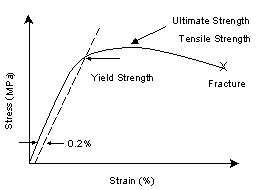


Efatigue Glossary Ultimate Strength



Motion Design 101 Stress Strain Curves Machine Design
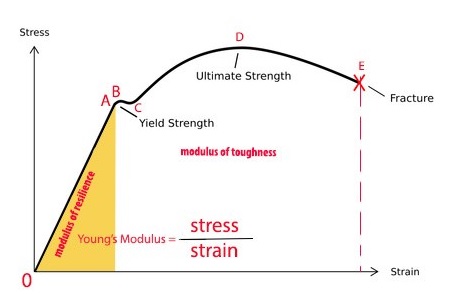


Exploring The Stress Strain Curve For Mild Steel The Chicago Curve



Types Of Strength Bortec
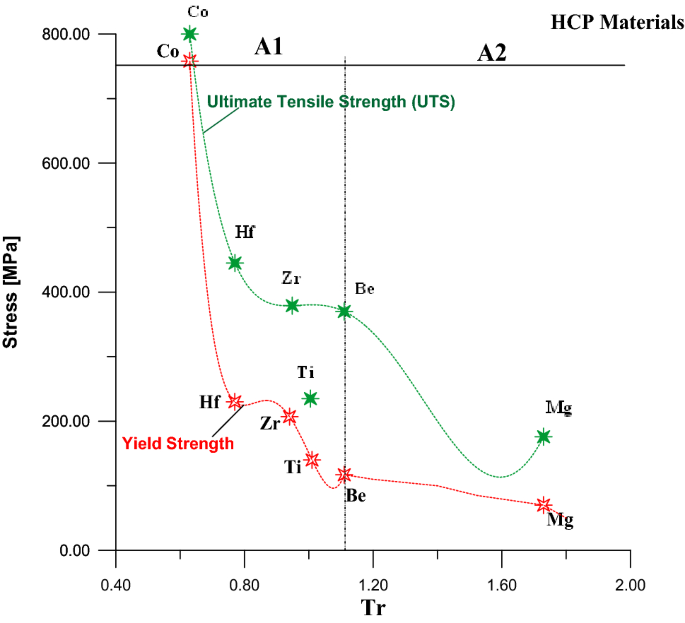


Estimation Of The Ultimate Tensile Strength And Yield Strength For The Pure Metals And Alloys By Using The Acoustic Wave Properties Scientific Reports



Stress Vs Strain Curve For Mild Steel Basic Mech In



Relationship Between Yield Stress Vs Fe H0 2 And Ultimate Tensile Download Scientific Diagram



Gizzet What Exactly Is Strength Blog
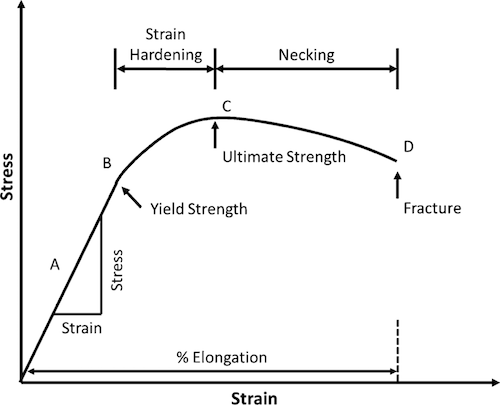


Cee 3710 Strength Versus Stiffness



Yield Strength



Stress Strain Curve Wikipedia


What Is The Difference Between Ultimate Stress And Yield Stress Quora


Www Usna Edu Naoe Files Documents Courses En380 Course Notes Ch10 Deformation Pdf


Q Tbn And9gcqdhkmo7hherjjmwerev9j1zxqfwpmjetj5gvnkildcbtyau41x Usqp Cau



Fastener Ultimate Tensile Strength Vs Yield Strength Which Is More Important Extreme Bolt


What Is The Basic Difference Between Yield Strength And Ultimate Strength For Any Elastic Material Quora



Ultimate Tensile Strength Uts Stress Strain Curve



Yield Engineering Wikipedia



Allowable Stress In Asme Viii 1 3 Api 650 Api 653 Amarine


Stress Strain Curve Explanation Stages Mild Steel Engineering Intro
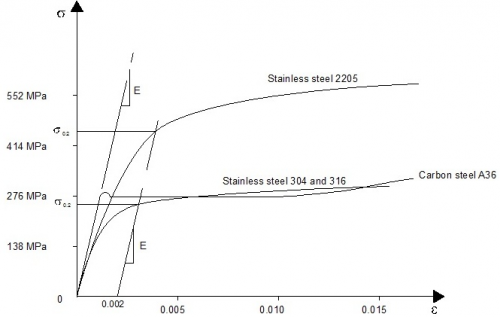


Steel Material Properties Steelconstruction Info
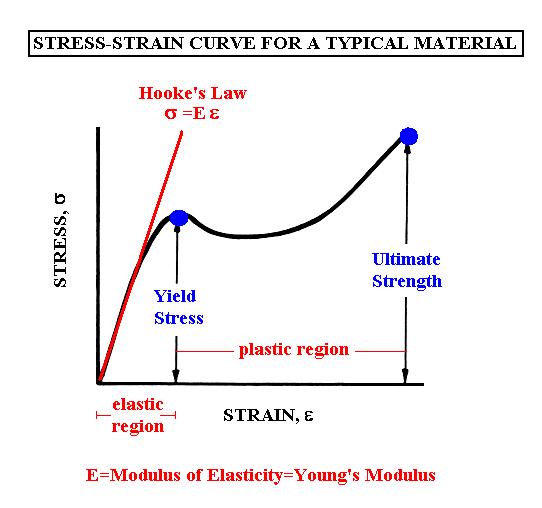


Strength


Q Tbn And9gcsubgeg9vwumror Qhoghyyxdjrgpugf4zei Gvjvgk9mt175y Usqp Cau


The Strain Rate Effect Of Engineering Materials And Its Unified Model



Smts And Allowable Stress Amarine



Stress Strain Curve An Overview Sciencedirect Topics


Q Tbn And9gctox3cf4zpt H1tpvycayerw3xbv Ukqszfzrag5mxfqpo7il42 Usqp Cau



Stress And Strain Mechanical Properties Of Materials



Engineering Stress Strain Curve Part One Total Materia Article


Tensile Testing
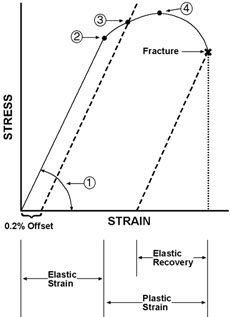


Industrial Design Guide Tensile Strength



Explanation Of Stress Strain Curve


Difference Between Yield Strength And Tensile Strength
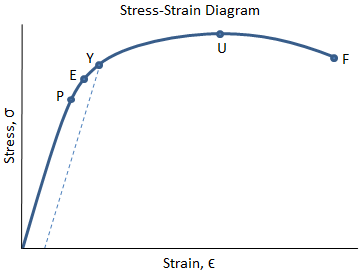


Mechanical Properties Of Materials Mechanicalc


What Is The Difference Between Ultimate Stress And Yield Stress Quora


Yield And Tensile Strength Engineering Materials Youtube


Thread Yield And Tensile Strength Equation And Calculator Engineers Edge Www Engineersedge Com
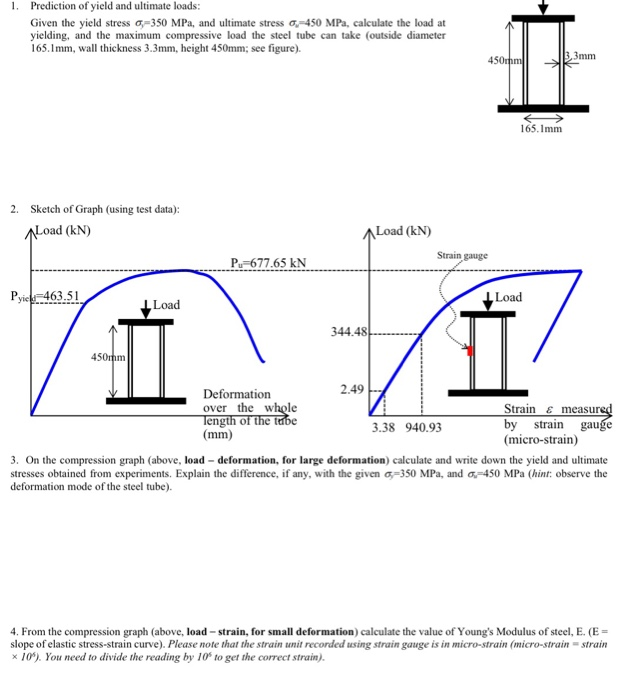


Solved 1 Prediction Of Yield And Ultimate Loads Given T Chegg Com


コメント
コメントを投稿